Bitcoin Halving – An Important Date
Table of Contents
If you’re curious to know all about the Bitcoin halving and the way it affects the price of Bitcoin, you’re at the right place.
Bitcoin halving is a process that occurs when 210,000 blocks have been recorded. Satoshi Nakamoto was the one who made this protocol from an integrated mechanism possible. Subsequently, this protocol cuts off the new supply of Bitcoins into two, so it was termed as “halving.” This process also halves the rewards of miner’s block production.
The Definition of Bitcoin Halving
Basically, the protocol of Bitcoin halving is cutting the Bitcoins’ reward into two. When miners verify their transactions, they will receive a half fewer Bitcoins when the protocol takes place.
If you are not familiar with Bitcoin I highly recommend to read our What is Bitcoin – Newbie Guide

Mining and Deflation: What Are They?
Rather than causing inflation, the 21 million under cap guarantees deflation in the economy. It’s because the core concept of Bitcoin is mining. You probably encountered this term and searched about it and its significance to Bitcoin.
For others who are not familiar with it, mining is a procedure wherein specific nodes or miners utilize a special mining device to decode difficult cryptographic puzzles.
Every transaction made on Bitcoin is compiled in a holding area called “Mempool”. Mempool is where all the transactions are going to be verified. The miners get these transactions here and create a block. The block will be included in the Bitcoin blockchain once the minimum requirements are fulfilled. You ought to remember that mining uses a lot of resources. Therefore, mining Bitcoins entail much spending and using money and electricity. It is able to motivate miners to go through the mining process because the block reward is believed to be economically beneficial.
In theory, the miners can gather all the Bitcoins around the globe if the mining mechanism is not halted. This can result in the alteration of the supply and demand equation.
Pretty interesting is the google trends chart for the keyword “Bitcoin halving” below. Look at the whole time range from 2014 until today. Wether it is a trend or not, the interest in the digital asset is without a doubt rising (Learn more about Digital Assets).
The 21 Million Upper Cap of Bitcoin
You might already be familiar with the 21 million upper cap Bitcoin has. If not, it means that only 21 million Bitcoins will be produced. You are probably wondering why Bitcoin has an upper cap limit. David Schwartz, who is the senior executive of Ripple, gave three reasons for this:
- By nature, the Fiat currency has extremely high inflation. Since the Federal Reserve is in charge of the US dollar, they can control the supply and introduce more cash in the system. Therefore, most people see this as something tremendously corrupt. This is the reason why Nakamoto made an upper cap that is difficult to encode so that no one can take advantage of inflating the supply of Bitcoins.
- It wasn’t sure if people would be able to adapt to the idea of Bitcoin when it was first introduced. Potential investors were encouraged to take hold of Bitcoins by establishing the supply of these coins.
- Lastly, policies were a must so that the currency can be distributed. To make this happen, miners will have to utilize computational power first. Transaction expenses can control and secure the Tokenomics of Bitcoin after mining all the coins.
Supply and Demand: A Quick Review
Let’s go on a basic economics detour before we continue talking about Bitcoin halving. One of the rudimentary microeconomics principles is the supply and demand model.
This model’s equation explains that in a competitive market where the components are equal, the prices of specific products differ until economic equilibrium is reached. To reach this equilibrium, the demand should be equal to the supply.
Therefore, there are two possible scenarios for this:
- If the demand is high and the supply is low, there is a price increase in a certain asset or product.
- If the demand is low, and the supply is high, there is a price decrease in a certain asset or product.
The prices of Bitcoins will cause a system crash if miners can mine Bitcoins purposelessly. It’s because the circulating supply will significantly increase. This is where Bitcoin halving comes into play. This hard-coded mechanism monitors the circulating supply.
Is It Possible for the Block Reward to Be Compensated by Transaction Fees?
Before answering this question, check this quick overview of the Bitcoin halving timeline:
- 2009- The process of Bitcoin mining started with 50 Bitcoins each block.
- 2012- The first Bitcoin halving occurred so that the mining rewards can be reduced to 25 Bitcoins.
- 2016- The second Bitcoin halving took place, so the mining rewards were lessened further to 12.5 Bitcoins.
- 2020- The third Bitcoin halving will happen, and mining rewards are expected to reduce to 6.25 Bitcoins.
Through this timeline, it can be estimated that around the year 2140, the 64th and last Bitcoin halving will take place. When the last Bitcoins are mined, the miners will have to depend on the transaction fees to earn rewards instead of blocks.
The value of rewards from transaction fees is way lower compared with blocks. Nevertheless, there was a time between December 2017 and January 2018 that the transaction fee rocketed to $54. The reason behind it isn’t complicated.
Imagine this. When there is an increase in demand, the number of transactions kept in the mempool also increases. Nevertheless, 1 Mb is the limited size per Bitcoin block. This means that each block can’t commit to a lot of transactions. The senders can pay more transaction fees to control it since miners will feel they are given preference through their incentives.
You can expect the demand for Bitcoin to increase in the year 2140 because of:
- No production of new coins- Because there will be no new coins to be produced in the market, the value of Bitcoins will be appreciated. Therefore, the overall demand for these coins will go up. Then, the transaction fees value goes up at the same time.
- Around the year 2140, the Bitcoins use cases will go up a little bit. The number of transactions also increases as the number of use cases goes up. This will result in a rise in transaction fees.
Stability of Mining Process
When determining the effect of Bitcoin halving, you must first check the mining process stability of the system. As mentioned, miners are vital in the overall operations of Bitcoin. Aside from helping in transactions and mining blocks, they also maintain the network. This is where the term “hashrate” comes in.
It is a network’s computational ability. The higher the security and speed of the network, the higher the hashrate is. Consequently, if the hashrate is lowered, the security and speed of the network are reduced as well.
The following may happen if the miners are not in the network:
- The system may get clogged up since no one mines the blocks and processes the transactions.
- A strong mining consortium with a high hashrate can take control of Bitcoin’s network by making a 51% attack.
In 2012 halving, there was an initial drop in the hashrate, but it was able to improve after four months. In the 2016 halving’s case, it improved after seven months. However, mining Bitcoins became less profitable after 2016.
You have to consider how miners adapt to Bitcoin halving when they depend on the block rewards to earn their income. Do they abandon the network or stay for its benefit?
The Profitability of Bitcoin

Various steps can be taken by miners to gain profit on Bitcoin. Here are some of them:
- Miners can use energy-saving programs such as Antminer S9 and Dragonmint T16. Since these programs have high-processing power output, there is lesser power consumption.
- They can transfer and operate in areas where there are inexpensive electricity and cold weather. There is drastically lesser energy consumption in cold places because of the cooling systems. That’s why some mining companies move their operations in Bratsk in Russia and Ulaanbaatar in Mongolia because of the cheap electricity and cold temperature. (Read more about how you can mine Bitcoins from home)
- They also convert their power source to alternative sources of energy to aid in their mining operations.
Bitcoin Halving & The Bitcoin Rates
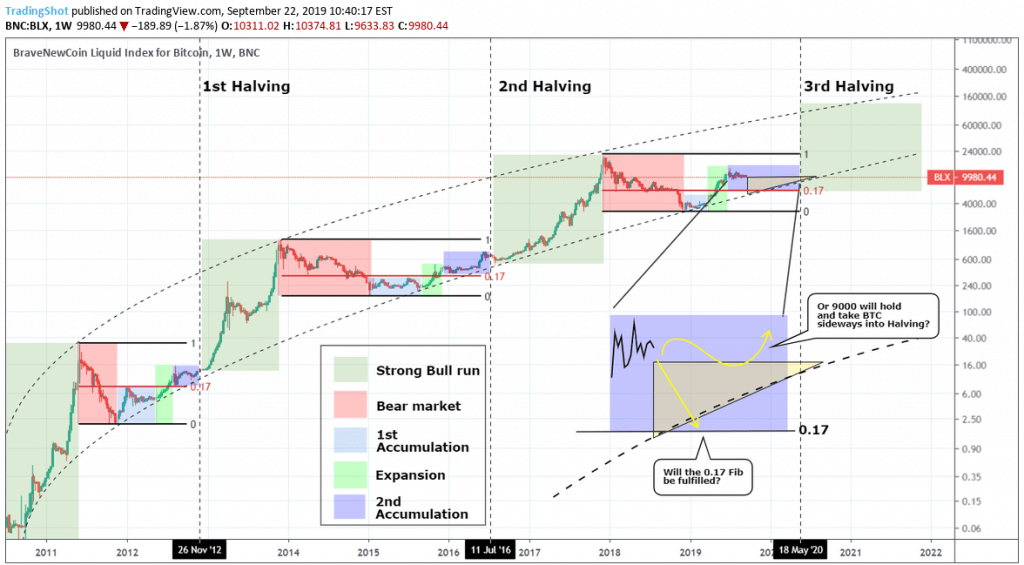
Does the price of Bitcoins go higher after the halving process? This is the most asked question. It’s because there was a little and quick Bitcoin/US dollar price increase after the halving event in 2012 before skyrocketing to $1,038 within a year. There was more than a 9 thousand percent increase.
In 2016, after 210,000 blocks were recorded, there was another price increase. In just a month, the value of the Bitcoin/US dollar went up to almost a hundred dollars due to buyers trying to accumulate Bitcoins for the purpose of halving. The price went up again to $2,526 after a year. Therefore, there was an over 200% increase in value.
The price increase in 2016 during Bitcoin halving was not as significant as the one that took place in 2012. Experts agree that this occurred because users were waiting eagerly for the halving event because of the expectation of price increase.
Because of this, it won’t come as a surprise if the reception of Bitcoin’s halving event in 2020 will be the same. Now, let’s see the opposite side of this equation. What arguments can possibly arise against the halving event in relation to the price of Bitcoins?
Can We Expect Changes in the Price?
To be honest, I don’t believe that anybody knows the answer to that question! There is much difference between how Bitcoin was in 2012 and 2016 and Bitcoin now. Some issues have to be taken into consideration to have comprehension as to why the halving event will not cause a significant change with the price:
- Just an assumption but Futures trading is now included in Bitcoin. This can result in the number of Bitcoins mined having less value because traders in the future don’t need actual Bitcoins to transact.
- When the market is up, miners may choose to sell their block rewards rather than keeping them.
- Compared to the total volume of coins traded, the amount of Bitcoins mined is meager. The ratio wasn’t distorted in 2012 and 2016, but, now, there are millions of Bitcoins traded each day. Therefore, there won’t be noticeable changes, even if the block reward is lessened from 12.5 to 6.25. The volume of Bitcoin trading is higher now due to the establishment of marketplace institutions.
Conclusion
Satoshi Nakamoto’s hard codes made it possible to secure all the Bitcoins that have been gathered. Subsequently, the network will be sustained through internal tokenomics.
To sum up, the core of the protocol is Bitcoin halving. When you think of it, this process guarantees that Bitcoin maintains its deflation rate. Halving also maintains its difference with Fiat currency since it naturally has high inflation and is controlled by a single entity.
For now, it’s really difficult to foresee if Bitcoin will be able to make 2012 and 2016 halving happen again. Will the value increase, or will the new factors affect it?
What do you think will happen? Leave a comment below!